Kenya is an East African Nation situated off the Indian Ocean; between Uganda to its west and Somalia to the east, north of Tanzania. The Country is traversed by the most prominent part of the Great Rift Valley which almost divides it into two equal parts. It is also home to Mount Kenya; the 2nd highest peak on the African continent at 5,199 meters.
Kenya is a former British Colony and attained its independence on the 12th of December 1963. Since its independence, the country was under single party rule with KANU (Kenya Africa National Union) as the sole political party accepted by the government. Jomo Kenyatta was the first Kenyan President and upon his death in 1978 was succeeded by Daniel Arap Moi.
President Moi ruled the country until 2002 when he retired from the political arena. Kenya currently has a multi-party democracy and constitutional reforms to further improve government dominate local politics.
Administration:
Kenya is divided into seven provinces and the Nairobi Area which includes the nation’s capital. The provinces are; Coast, Nyanza, Eastern, North Eastern, Western, Central and Rift Valley. The City of Nairobi is the Capital of Kenya.
People:
Kenya has an estimated population of 34, 707, 817 people. English and Swahili are the Country’s official languages. Christianity is the main religion though others such as Islam, Hindu and Indigenous beliefs are practiced.
The Kenyan Flag:
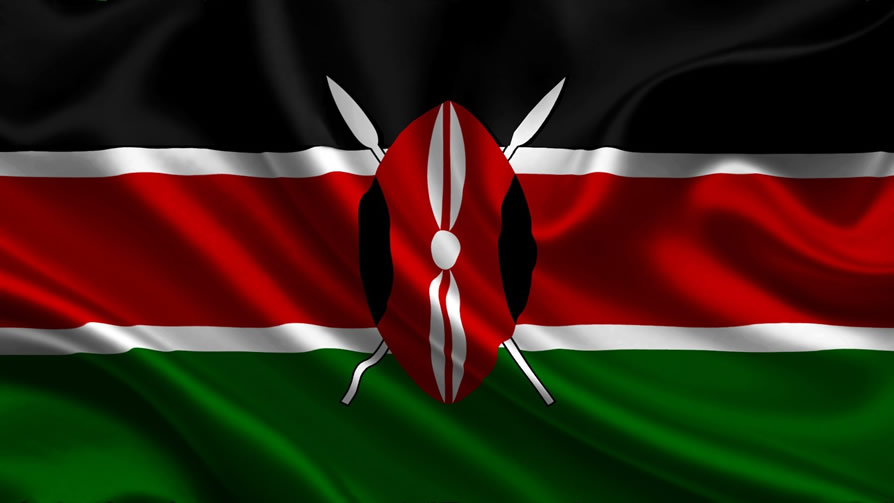

The colors on the Kenyan Flag are based on those of the KANU Flag; the political party which led the country to independence. The flag was adopted on the 12th of December 1963 when the country attained its independence.
The black color represents the color of the nation’s people, white is for peace, green is for the land and red is for the blood shed for the country’s independence. The traditional Masai shield with two spears at the center represents the readiness to defend the aforementioned representations.
Kenya Government:
Kenya has a multi-party democratic government which supports a healthy political environment. The first multi-party elections were held in 1992 and won by KANU under the leadership of Daniel arap Moi. KANU’s domination of government ended in 2002 when a coalition of opposition parties (National Rainbow Coalition) led by Mwai Kibaki won the elections.
This coalition however began to disintegrate soon after the elections with some parties feeling left out of the newly formed government. The next elections are to be held in 2007. Major political parties in the country include; LDP (Liberal Democratic Party), Ford Kenya, Ford People, Democratic Party, KANU.
Constitutional reforms are a major issue for the current government. According to the current constitution; presidential and parliamentary elections are to be held every five years. A president is only allowed to rule for two terms.
Kenya History:
Modern Kenyan History begins at around the 15th Century when the Portuguese first arrived at the East Coast of Africa. Trade along the coastline led to the development of settlements and eventually towns such as Lamu, Mombasa and Malindi. The Portuguese were eventually expelled from the Coast in the 18th century by the Omani Arabs.
The British first arrived in 1888 when the Imperial British East Africa Protectorate was established. The Kenya-Uganda Railway was built by the British to make the interior more accessible. The British colonial rule met armed resistance by the Mau Mau Freedom Fighters between 1952 and 1959 a period in which the country was placed under a state of emergency. The Mau Mau rebellion was eventually suppressed by the Colonial government.
Political parties such as the Kenya Africa Union (KAU) and Kenya Africa National Union (KANU) emerged and began to lobby for increased rights for the Kenyan people. Kenya eventually attained its independence from the British on the 12th of December 1963 with Jomo Kenyatta as the first President.
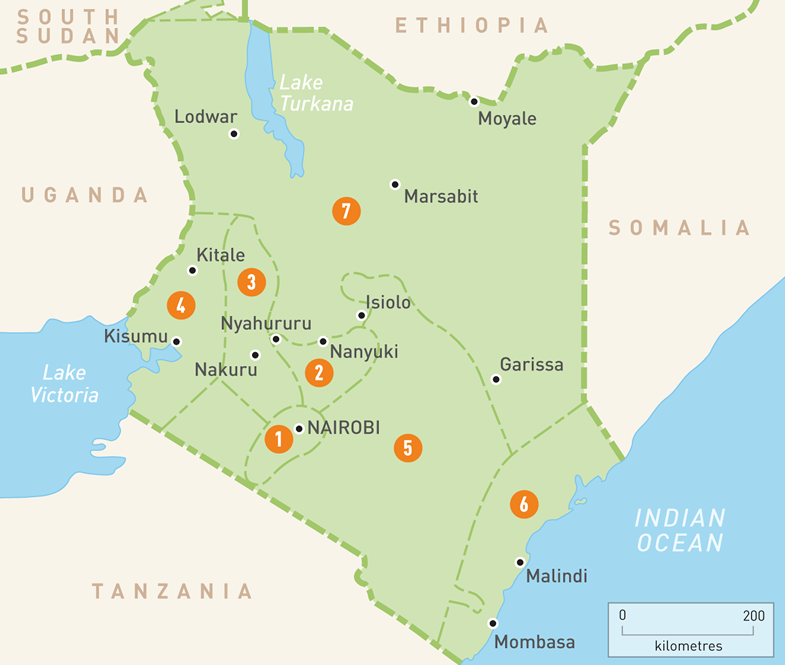
Map of Kenya:
Kenya Currency:
The Kenyan Shilling was adopted from the British Shilling and replaced the East African Shilling in 1966. The Currency features the images of Presidents past and present and words are in English and Swahili. The release of the currency and exchange rates are controlled by the Central Bank of Kenya; a regulatory body. 1 shilling is equivalent to 100 cents.
Denominations:
Coin denominations exist for; 50 cents, 1, 5, 10, 20 and 40 shillings. Notes exist for 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1000 shillings.
Exchange rates against major currencies:
At the time of writing (July, 2006); 1 American Dollar was equivalent to 73.7 Shillings, 1 British Pound was equivalent to 135.99 Shillings and 1 Euro was equivalent to 94.13 Shillings.
Kenya Facts & Figures:
– Location: Eastern Africa, off the Indian Ocean, east of Uganda, west of Somalia.
– Capital City: Nairobi.
– Population: 34, 707, 817.
– Other major towns and cities: Nakuru, Eldoret, Lamu, Malindi, Nyeri, Kisumu, Kakamega, Mombasa, Naivasha.
– Religion: Christian, Islam, Hindu, Traditional, Others.
– Languages: English, Swahili are the official languages, Indigenous.
– Currency: Kenyan Shilling (Ksh).
Public Holidays in Kenya:
There are a number of public holidays observed in a calendar year. Christian and Muslim religious holidays are also observed. These include; Christmas, Easter and Idd Ul Fitr which is the end of the Ramadan.
Public holidays normally affect the opening of businesses and some services, though small shops, some restaurants and pubs usually open.
Public holidays in Kenya are:
New Years Day on the 1st of January.
Labor Day on the 1st of May.
Madaraka Day on the 1st of June.
Moi Day on the 10th of October.
Kenyatta Day on the 20th of October.
Jamhuri (Independence) Day on the 12th of December.
Education in Kenya:
Education in Kenya was initially based on the British System, before the now operational 8-4-4 system was adopted. The Country was the first in Africa to introduce free primary education as part of pre-electoral promises made by President Mwai Kibaki. Kenya also has a host of public and private universities and specialist institutes of higher learning.
The bulk of the Country’s universities and colleges are situated in the Kenyan Capital Nairobi.
Universities in Kenya:
– Nairobi University,
– Egerton University,
– Kenyatta University,
– Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology,
– Nazarene University,
– Strathmore University,
– United States International University (USIU),
– Daystar University,
– Moi University.
Health in Kenya:
HIV/AIDS is the biggest health risk in Kenya. The disease was declared a national disaster by former President; Daniel Moi. The disease affects close to 7 % of the Country’s population and there are over 1 million people living with the condition. Other health problems are; water and food hygiene; Safe drinking water especially out of major towns is hard to come by. Bottled water is easily available from kiosks and supermarkets. Malaria is still a major problem though the disease can be easily overcome by taking anti-malarial medication prior to travel.
Hospitals and health centers:
Kenya has a reasonably developed health infrastructure. The Country has hospitals at district and provincial levels. Clinics and health centers also exist in the smaller towns. Major cities such as Nairobi and Mombasa have the best health facilities in the Country. Nairobi has some of the leading hospitals in East Africa such as; the Kenyatta Hospital, Nairobi Hospital and the Aga Khan Hospital.
Hospitals in Mombasa include; the Mombasa Hospital, Aga Khan Hospital, Diani Beach Hospital and the Pandya Memorial Hospital.
Food in Kenya:
Ugali: Ugali is the national food in Kenya, eaten by most people in the country regardless of ethnic background and class. Ugali is prepared by mixing maize flour with boiling water to a pasty semi-hard mixture. Ugali is not eaten on its own and is used together with stews or/and vegetables.
Githeri: a popular dish which has slowly gained national appeal due to its high energy content. Githeri is a traditional kikuyu dish consisting of maize and beans. Vegetables can also be added to the meal.
Chapati: a disk like bread made from wheat flour, Chapati is a result of Indian influences in local Kenyan cuisine and is popular around the country.
A variety of foods including fresh fruits and vegetables are available in the country. These are sold at local markets and availability depends on the season. Fresh meat is sold at butcheries and fresh seafood mainly from Lake Victoria is readily available.
Restaurants:
There is a wide range of cuisines and restaurants especially in the large cities such as Mombasa, Nairobi and Kisumu. Here you can find a range of restaurants and fast food joints including; American, Italian, Japanese, Indian, Chinese, African, Korean, Mexican and English.
Sports in Kenya:
Kenya is one of Africa’s leading sporting nations. The Country has for years featured prominently at the Olympic Games, Commonwealth Games and Athletic Championships. Kenya has produced a number of World famous athletes who have dominated middle and long distance races such as; Kipchoge Keino, Naftali Temu, Moses Kiptanui, Douglas Wakihuri, John Ngugi, Moses Tanui and Paul Kipkoech. The 3,000 meters steeplechase is a special event and the country has dominated winning the gold medal at major meets.
Soccer:
The National Soccer Team known as “Harambee Stars” is one of the stronger teams in East and Central Africa. The team competes regularly at regional tourneys and has also participated at the African Nation’s Cup and World Cup Qualifiers. The Country also has a healthy club competition though local clubs such as Gor Mahia once Continental Champions and AFC Leopards are not as dominant.
Volleyball:
Kenyan clubs as well as the national team both men and women are major competitors in continental competitions. The women’s national team has represented the continent at the world cup.
Cricket:
The Kenyan Cricket team has participated at the last three world cups. Opponents know never to underestimate the Kenyans. The team’s first scalp was West Indies at the 1996 world cup in Pakistan. The team lost all its matches at the 1999 tournament. In 2003, Kenya surprised everyone by beating Sri Lanka, Canada and Bangladesh on their way to the Semi Finals where the team lost to India.
Rugby:
The Kenya Cup is the main rugby league in Kenya and features prominent clubs such as Impala, Nondescripts, Harlequins, Mwamba and Mean Machine. The sport is the fastest growing team sport in the country and is played in many schools and colleges. The National Sevens Team participates on the international circuit.
Newspapers in Kenya:
Kenya has a relatively liberal print media. Government interference in local media occurs though not as often as in other nations in the region. Local newspapers usually carry investigative reports which reveal scandals in government. Magazines and newspapers are written in English and Swahili though a number of tribal publications exist. Popular newspapers in the country are;
Media
Nation Newspapers:
Run by the Nation Media Group; the largest media house in East Africa, Nation Newspapers include the Daily Nation, the East African both English papers and Taifa Leo which is a Swahili version. Both these papers are popular and are available online.
The East African Standard:
Also available online; the East African Standard is one of the oldest papers in the Country. The paper rivals the Daily Nation in terms of popularity.
Kenya Times: A government owned paper; Kenya Times is also available online. The paper has however diminished greatly in popularity since KANU was voted out of power in 2002.
Radio in Kenya:
There are a number of radio stations in Kenya, many broadcasting on Fm frequencies. Some of the larger stations such as those run by the Kenya Broadcasting Corporation have a nationwide reach. Most stations broadcast in English and Swahili, though indigenous stations are popping up around the Country. Popular stations in the country are;
Nation Fm: with a nationwide audience, Nation Fm is a recent entrant to the broadcasting media arena. The station is operated by the Nation Media Group and is also available online for international listeners.
Capital Fm: a popular station especially within Nairobi, the station is available online.
Other popular stations are; Kiss Fm, Kameme Fm, Citizen Fm, KBC Swahili and English Services.
Tv in Kenya:
KTN (Kenya Television Network): is one of the leading television stations in the country established in the early 1990s. The station transmits from Nairobi to other parts of the country including western Kenya and the coast.
Nation TV: owned by the Nation Media Group, Nation TV is a popular station with an almost nationwide coverage.
KBC (Kenya Broadcasting Corporation): a government run station, KBC was introduced to replace the Voice of Kenya (VOK). The Station has nationwide coverage.
Mnet: a cable television company from South Africa. The service is especially popular for its sports broadcasts and many bars and pubs have Mnet to provide their clientele with international sporting entertainment.
Other television stations are; Citizen TV, Family TV, STV.
Tours & Travel
Flights to Kenya:
A result to its prominence as a leading tourism destination is the fact that a good number of airlines fly regularly to Kenya. The Country has three international airports; Jomo Kenyatta in Nairobi, Moi International in Mombasa and the Eldoret International Airport.
The Wilson Airport in Langata, Nairobi is one of the busiest light aircraft hubs in Africa. The airport caters for small chartered flights and most notably; the Flying Doctors service.
Kenya Airways is the national airline and flies to a number of domestic and international destinations from its main hub at the Jomo Kenyatta Airport.
Other airlines flying regularly to Kenya are; Emirates, British Airways, Ethiopian Airlines, KLM, Swiss International, Air Madagascar, Air Mauritius, Air India, Air Tanzania, Air Zimbabwe, Air Seychelles, South African Airways, Gulf Air, Qatar Airways, Sudan Airways.
Kenya Airways:
Kenya Airways is one of the leading airlines in Africa and the national flag carrier of Kenya. The airline was formed in 1977 following the disintegration of East African Airlines. The airline was owned by the Kenyan Government until the early 1990s when it was commercialized.
Kenya Airways conducts a number of regular scheduled flights from its main hub at the Jomo Kenyatta International Airport in Nairobi. The airline flies to a number of domestic and international destinations including;
Domestic: Mombasa, Lamu, Kisumu, Lokichoggio, Nairobi.
International: Abidjan, Addis Ababa, Amsterdam, Bamako, Bangkok, Bujumbura, Cairo, Cape Town, Dakar, Dar es Salaam, Djibouti, Douala, Entebbe, Freetown, Harare, Hong Kong, Guangzhou, Istanbul, Johannesburg, Khartoum, Kigali, Kinshasa, Lagos, Lilongwe, London, Lubumbashi, Lusaka, Mahe, Maputo, Mumbai, Yaounde,Zanzibar.
Kenyan Safari:
Kenyan Safaris feature prominently on many of the country’s visitors plans. The Country’s tourism industry is a major foreign exchange earner and Kenya is one of the leading holiday destinations on the African continent. Kenyan Safaris offer visitors the unique chance to view a magnificent display of wildlife in their natural habitat. Packaged tours are offered and trips can be tailored to suit preferences.
The Country has more than 40 game parks and reserves many of which feature a healthy wildlife population which features the big five; Rhino, Elephant, Buffalo, Lion and Leopard. Kenya has some of the most popular nature parks in Africa such as the Amboseli, Tsavo, Aberdares, Lake Nakuru and Masai Mara.
Most parks in the country are accessible by road though chartered flights are available from the Wilson Airport in Nairobi as many parks have their own airstrips. Accommodation is available and there are a number of exceptional options including game lodges and tented camps. These offer a unique quality accommodation within the wilderness and some are amply located with views to water holes visited regularly by wildlife.
You can create your own Kenyan Safari experience by either touring on foot with a traditional guide, travel by vehicle or balloon safaris which are becoming a popular option.
Mount Kenya:
Mount Kenya is the 2nd highest mountain on the African Continent after Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania. The Mountain stands at a height of 5,199 meters above sea level. The mountain is an extinct volcano with permanent glacial cover situated in central Kenya about 180 km from Nairobi. The mountain is easily reachable by road from Nairobi, though air transport from the Wilson airport is available to Nanyuki Town.
The Mount Kenya National Park:
The Mountain is encompassed by the Mount Kenya National Park; a protected area under the management of the Kenya Wildlife Service. The Park features a variety of wildlife including; elephant, leopard, colobus monkey, black rhino, baboon, hyena, zebra, waterbuck and forest antelope.
The mountain is also a popular destination for hikers and climbers and its peaks offer a reasonable challenge even for experienced climbers.
Accommodation:
There are a number of quality accommodation options near the mountain such as; the Mount Kenya Safari Club, Mountain Lodge, Outspans and the Treetops Lodge.
Consular Services
Embassy Directory:
Kenyan Embassies and Consulates in Australasia:
Kenyan Embassy in Australia:
Address: 6th Floor, O.B.E Building
Ainslie Avenue 33-35
G.P.O Box 1990, Canberra, A.C.T. 2601
Australia.
Tel: 61 026 247 4788.
Kenyan Embassy in China:
Address: 4XI Liu Jie San Li Tun,
Beijing, 100600 China
Tel: 86 1- 6532 3381
Kenyan Embassy in Pakistan:
Address: House No. 10, Street No. 9 Sector F-7/3
P.O. Box 2097, Islamabad, Pakistan
Tel: 92 51 279 540.
Kenyan Embassy in Malaysia:
Address: Empire Tower, Unit 38 C, 38th Floor,
182 Jalan Tun Razak
50450 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Tel: 60 3 216 45 015.
Kenyan Embassy in India:
Address: 34, Paschimi Marg, Vasant Vihar,
New Delhi, 110057 India.
Tel: 91 11 261 46 537.
Kenyan Embassy in Japan:
Address: No. 24-3 Yakumo, 3 Chome,
Meguro-Ku, Tokyo 152, Japan
Tel: 81 3 372 34 006/7.
Kenyan Embassies and Consulates in Europe:
Kenyan Embassy in the United Kingdom:
Address: 45 Portland Place, London W1N 4AS
Tel: 020 7636 2371/5
Kenyan Embassy in France:
Address: 3 Rue Freycinet, 75116, Paris France.
Tel: 000 331 566 225 525
Kenyan Mission to the European Union:
Address: Avenue Winston Churchill 208,
1180 Brussels, Belgium.
Tel: 000 32 2 340 1040
Kenyan Mission to the United Nations:
Address: 1-3 Avenue De La Paix,
1202 Geneva, Switzerland.
Tel: 000 41 22 906 4050.
Kenyan Embassy in the Netherlands:
Address: Nieuwe Parklaan 21,
2597 La The Hague, Netherlands.
Tel: 31 70 350 4215.
Kenyan Embassy in Russia:
Address: Bolshaya Ordinka, Dom, 70,
Moscow, Russia
Tel: 7 095 237 4702/ 3462/ 4501.
Kenyan Embassy in Italy:
Address: Via Archimede 164
00197 Roma, Italy
Tel: 39 06 808 2717.
Kenyan Embassy in Sweden:
Address: Birger Jarlsgatan 37, 2nd Floor
P.O Box 7694
103 95 Stockholm, Sweden
Tel: 46 8 218 300.
Kenyan Embassy in Austria:
Address: Neulinggasse 29/8
1030 Vienna, Austria
Tel: 43 1 712 3919.
Kenyan Embassies and consulates in North America:
Kenyan Mission to the United Nations:
Address: 866 U.N. Plaza, Suite 486,
New York, NY 10017, USA
Tel: 1 212 421 4740.
Kenyan Embassy in Canada:
Address: 415 Laurier Avenue East Ottawa,
Ontario KIN 6R4 Canada
Tel: 1 613 563 1773.
Kenyan Embassy in the United States:
2249 R. Street, N.W
Washington D.C. 20008, USA
Tel: 1 202 387 6101.

